Focused On-demand Libraries - Receptor.AI Collaboration
Explore the Potential with AI-Driven Innovation
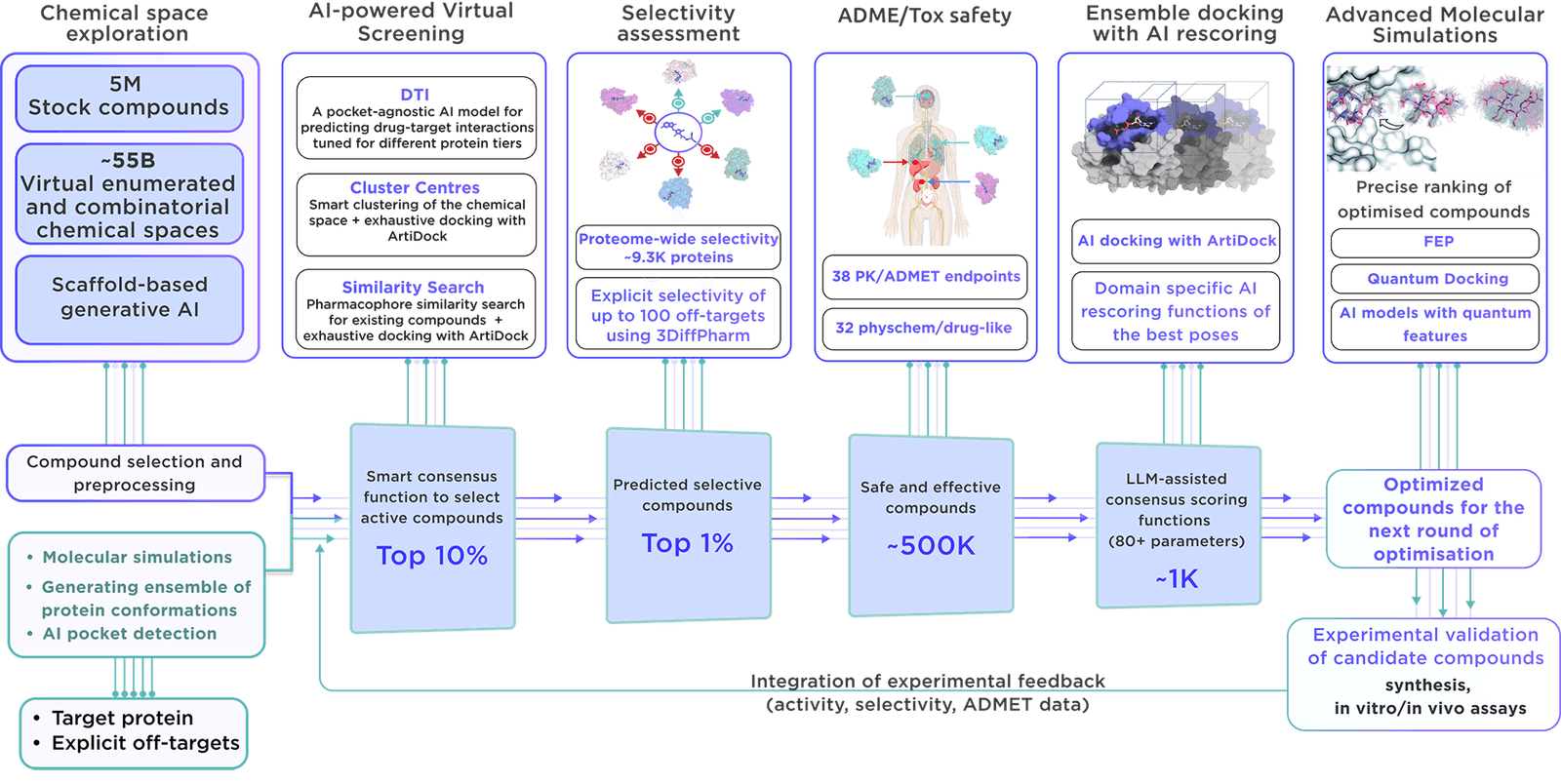
The specialised, focused library is developed on demand with the most recent virtual screening and parameter assessment technology, guided by the Receptor.AI drug discovery platform. This approach exceeds the capabilities of traditional methods and offers compounds with higher activity, selectivity, and safety.
From a virtual chemical space containing more than 60 billion molecules, we precisely choose certain compounds. Reaxense aids in their synthesis and provision.
Contained in the library are leading modulators, each labelled with 38 ADME-Tox and 32 physicochemical and drug-likeness qualities. In addition, each compound is illustrated with its optimal docking poses, affinity scores, and activity scores, giving a complete picture.
We employ our advanced, specialised process to create targeted libraries for enzymes.
It includes comprehensive molecular simulations of the catalytic and allosteric binding pockets and the ensemble virtual screening accounting for their conformational mobility. In the case of designing modulators, the structural changes induced by reaction intermediates are taken into account to leverage activity and selectivity.
Key features that set our library apart include:
- The Receptor.AI platform integrates extensive information about the target protein, such as historical experiments, academic research, known ligands, and structural insights, thereby increasing the likelihood of identifying highly relevant compounds.
- The platform’s sophisticated molecular simulations are designed to discover potential binding sites, ensuring that our focused library is optimal for the discovery of allosteric inhibitors and binders for cryptic pockets.
- With over 50 customisable AI models, verified through extensive testing in commercial drug discovery and research, Receptor.AI is efficient, reliable, and precise. These models are essential in the production of our focused libraries.
- Receptor.AI not only produces focused libraries but also provides full services and solutions at every stage of preclinical drug discovery, with a success-based pricing structure that aligns our interests with the success of your project.
Receptor.AI
O60774
UPID:
FMO6_HUMAN
ALTERNATIVE NAMES:
Dimethylaniline oxidase 6; Flavin-containing monooxygenase 6
ALTERNATIVE UPACC:
O60774