Focused On-demand Libraries - Receptor.AI Collaboration
Explore the Potential with AI-Driven Innovation
The specialised, focused library is developed on demand with the most recent virtual screening and parameter assessment technology, guided by the Receptor.AI drug discovery platform. This approach exceeds the capabilities of traditional methods and offers compounds with higher activity, selectivity, and safety.
Our selection of compounds is from a large virtual library of over 60 billion molecules. The production and distribution of these compounds are managed by Reaxense.
Contained in the library are leading modulators, each labelled with 38 ADME-Tox and 32 physicochemical and drug-likeness qualities. In addition, each compound is illustrated with its optimal docking poses, affinity scores, and activity scores, giving a complete picture.
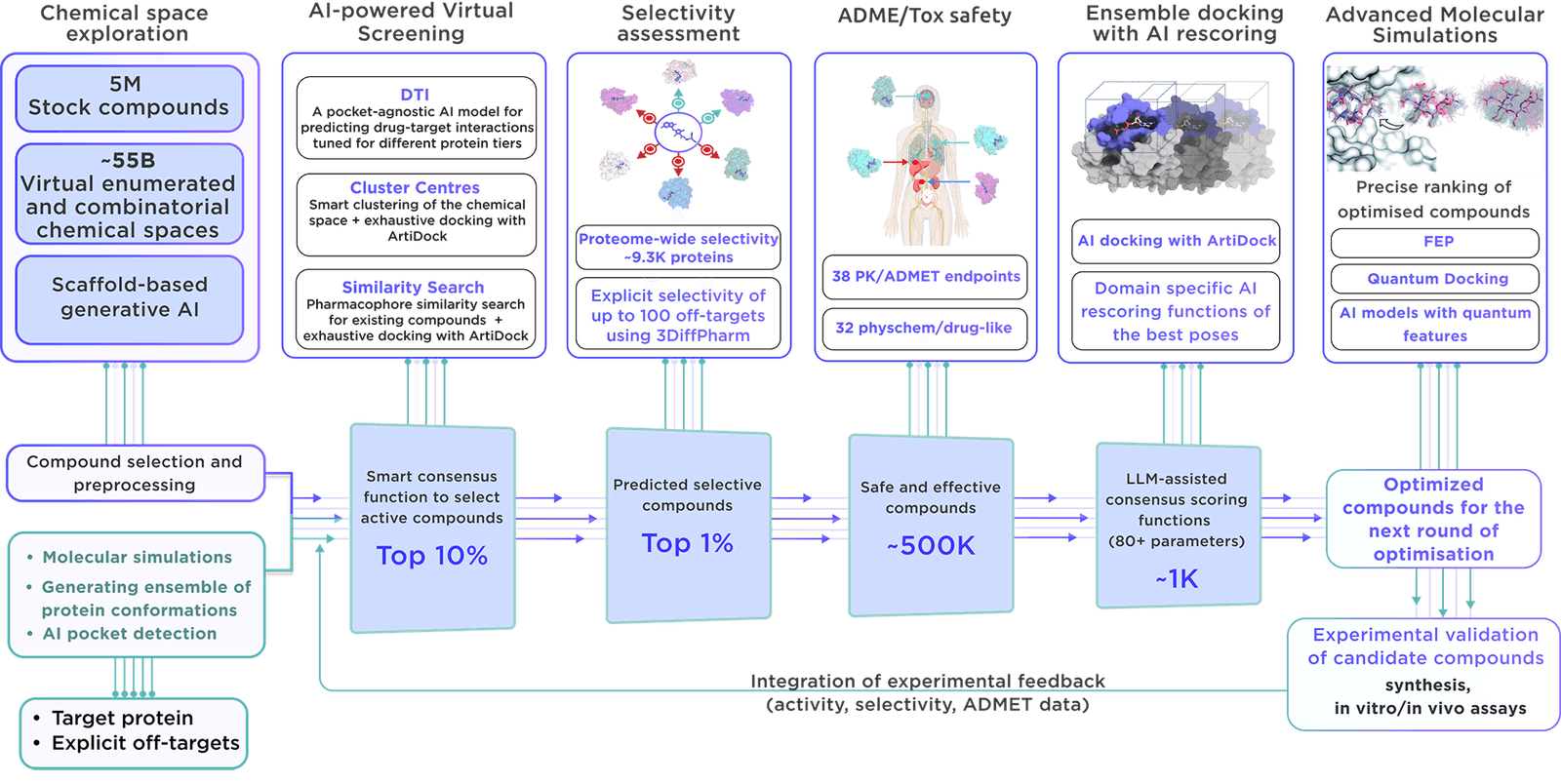
Our high-tech, dedicated method is applied to construct targeted libraries.
Our methodology employs molecular simulations to explore a wide array of proteins, capturing their dynamic states both individually and within complexes. Through ensemble virtual screening, we address conformational mobility, uncovering binding sites within functional regions and remote allosteric locations. This thorough exploration ensures no potential mechanism of action is overlooked, aiming to discover novel therapeutic targets and lead compounds across an extensive spectrum of biological functions.
Our library stands out due to several important features:
- The Receptor.AI platform compiles comprehensive data on the target protein, encompassing previous experiments, literature, known ligands, structural details, and more, leading to a higher chance of selecting the most relevant compounds.
- Advanced molecular simulations on the platform help pinpoint potential binding sites, making the compounds in our focused library ideal for finding allosteric inhibitors and targeting cryptic pockets.
- Receptor.AI boasts over 50 tailor-made AI models, rigorously tested and proven in various drug discovery projects and research initiatives. They are crafted for efficacy, dependability, and precision, all of which are key in creating our focused libraries.
- Beyond creating focused libraries, Receptor.AI offers comprehensive services and complete solutions throughout the preclinical drug discovery phase. Our success-based pricing model minimises risk and maximises the mutual benefits of the project's success.
Receptor.AI
P21462
UPID:
FPR1_HUMAN
ALTERNATIVE NAMES:
N-formyl peptide receptor; N-formylpeptide chemoattractant receptor
ALTERNATIVE UPACC:
P21462; Q14939; Q7Z6A4; Q86U52; Q9NS48