Focused On-demand Libraries - Receptor.AI Collaboration
Explore the Potential with AI-Driven Innovation
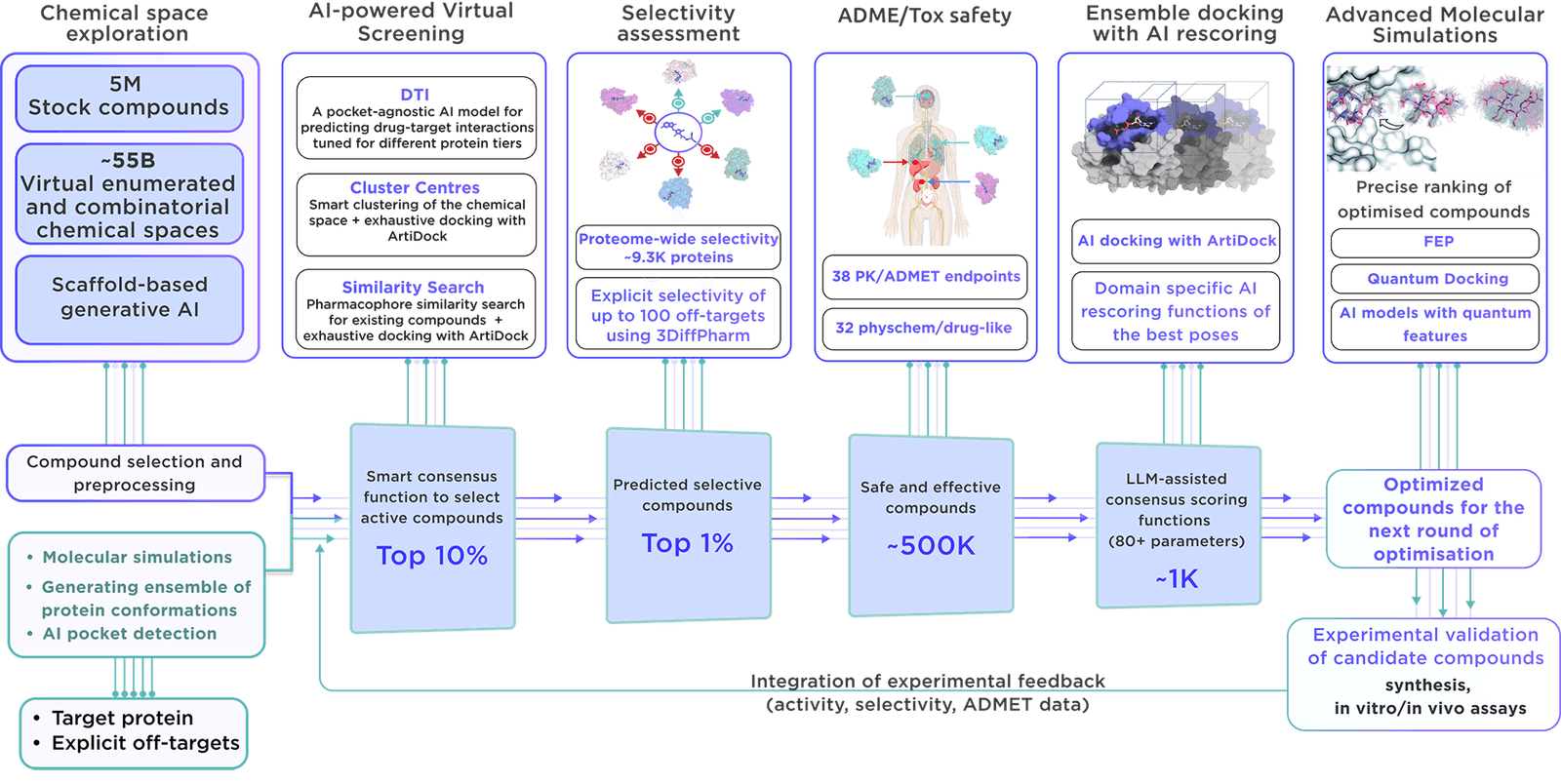
The specialised, focused library is developed on demand with the most recent virtual screening and parameter assessment technology, guided by the Receptor.AI drug discovery platform. This approach exceeds the capabilities of traditional methods and offers compounds with higher activity, selectivity, and safety.
From a virtual chemical space containing more than 60 billion molecules, we precisely choose certain compounds. Reaxense aids in their synthesis and provision.
The library includes a list of the most promising modulators annotated with 38 ADME-Tox and 32 physicochemical and drug-likeness parameters. Also, each compound is presented with its optimal docking poses, affinity scores, and activity scores, providing a comprehensive overview.
Our high-tech, dedicated method is applied to construct targeted libraries.
By deploying molecular simulations, our approach comprehensively covers a broad array of proteins, tracking their flexibility and dynamics individually and within complexes. Ensemble virtual screening is utilised to take into account conformational dynamics, identifying pivotal binding sites located within functional regions and at allosteric locations. This thorough exploration ensures that every conceivable mechanism of action is considered, aiming to identify new therapeutic targets and advance lead compounds throughout a vast spectrum of biological functions.
Our library distinguishes itself through several key aspects:
- The Receptor.AI platform integrates all available data about the target protein, including past experiments, literature data, known ligands, structural information and more. This consolidated approach maximises the probability of prioritising highly relevant compounds.
- The platform uses sophisticated molecular simulations to identify possible binding sites so that the compounds in the focused library are suitable for discovering allosteric inhibitors and the binders for cryptic pockets.
- The platform integrates over 50 highly customisable AI models, which are thoroughly tested and validated on a multitude of commercial drug discovery programs and research projects. It is designed to be efficient, reliable and accurate. All this power is utilised when producing the focused libraries.
- In addition to producing the focused libraries, Receptor.AI provides services and end-to-end solutions at every stage of preclinical drug discovery. The pricing model is success-based, which reduces your risks and leverages the mutual benefits of the project's success.
Receptor.AI
P27348
UPID:
1433T_HUMAN
ALTERNATIVE NAMES:
14-3-3 protein T-cell; 14-3-3 protein tau; Protein HS1
ALTERNATIVE UPACC:
P27348; D6W4Z5; Q567U5; Q5TZU8; Q9UP48