Focused On-demand Libraries - Receptor.AI Collaboration
Explore the Potential with AI-Driven Innovation
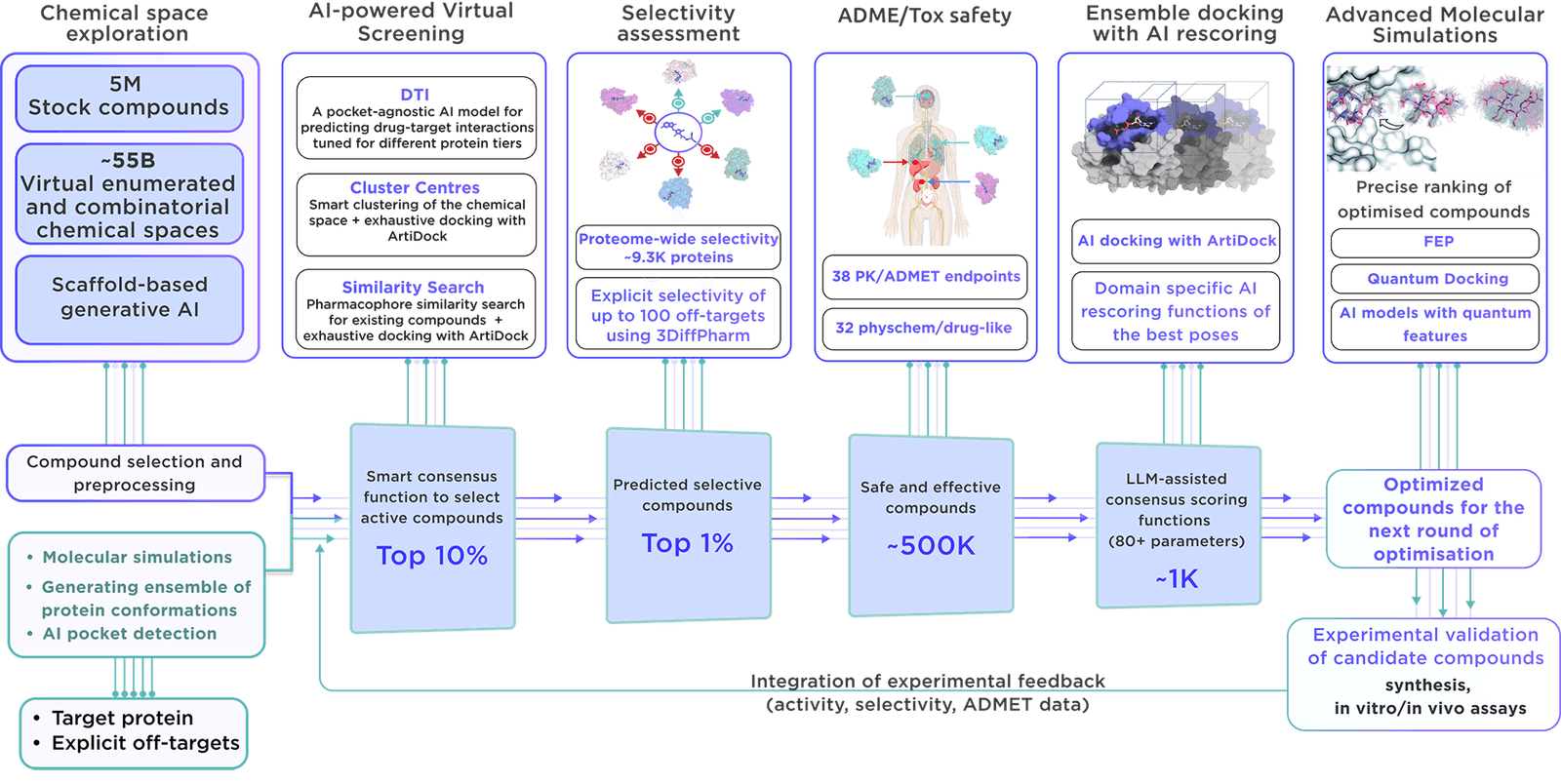
The focused library is created on demand with the latest virtual screening and parameter assessment technology, supported by the Receptor.AI drug discovery platform. This method is more effective than traditional methods and results in higher-quality compounds with better activity, selectivity, and safety.
From a virtual chemical space containing more than 60 billion molecules, we precisely choose certain compounds. Reaxense aids in their synthesis and provision.
Contained in the library are leading modulators, each labelled with 38 ADME-Tox and 32 physicochemical and drug-likeness qualities. In addition, each compound is illustrated with its optimal docking poses, affinity scores, and activity scores, giving a complete picture.
We employ our advanced, specialised process to create targeted libraries for enzymes.
The method includes detailed molecular simulations of the catalytic and allosteric binding pockets, along with ensemble virtual screening that considers their conformational flexibility. In the design of modulators, structural changes induced by reaction intermediates are taken into account to enhance activity and selectivity.
Our library is unique due to several crucial aspects:
- Receptor.AI compiles all relevant data on the target protein, such as past experimental results, literature findings, known ligands, and structural data, thereby enhancing the likelihood of focusing on the most significant compounds.
- By utilizing advanced molecular simulations, the platform is adept at locating potential binding sites, rendering the compounds in the focused library well-suited for unearthing allosteric inhibitors and binders for hidden pockets.
- The platform is supported by more than 50 highly specialized AI models, all of which have been rigorously tested and validated in diverse drug discovery and research programs. Its design emphasizes efficiency, reliability, and accuracy, crucial for producing focused libraries.
- Receptor.AI extends beyond just creating focused libraries; it offers a complete spectrum of services and solutions during the preclinical drug discovery phase, with a success-dependent pricing strategy that reduces risk and fosters shared success in the project.
Receptor.AI
Q9BSE5
UPID:
GDAH_HUMAN
ALTERNATIVE NAMES:
Arginase, mitochondrial; Guanidinobutyrase, mitochondrial; Guanidinopropionase, mitochondrial
ALTERNATIVE UPACC:
Q9BSE5; Q5TDH1; Q9H5J3