Focused On-demand Libraries - Receptor.AI Collaboration
Explore the Potential with AI-Driven Innovation
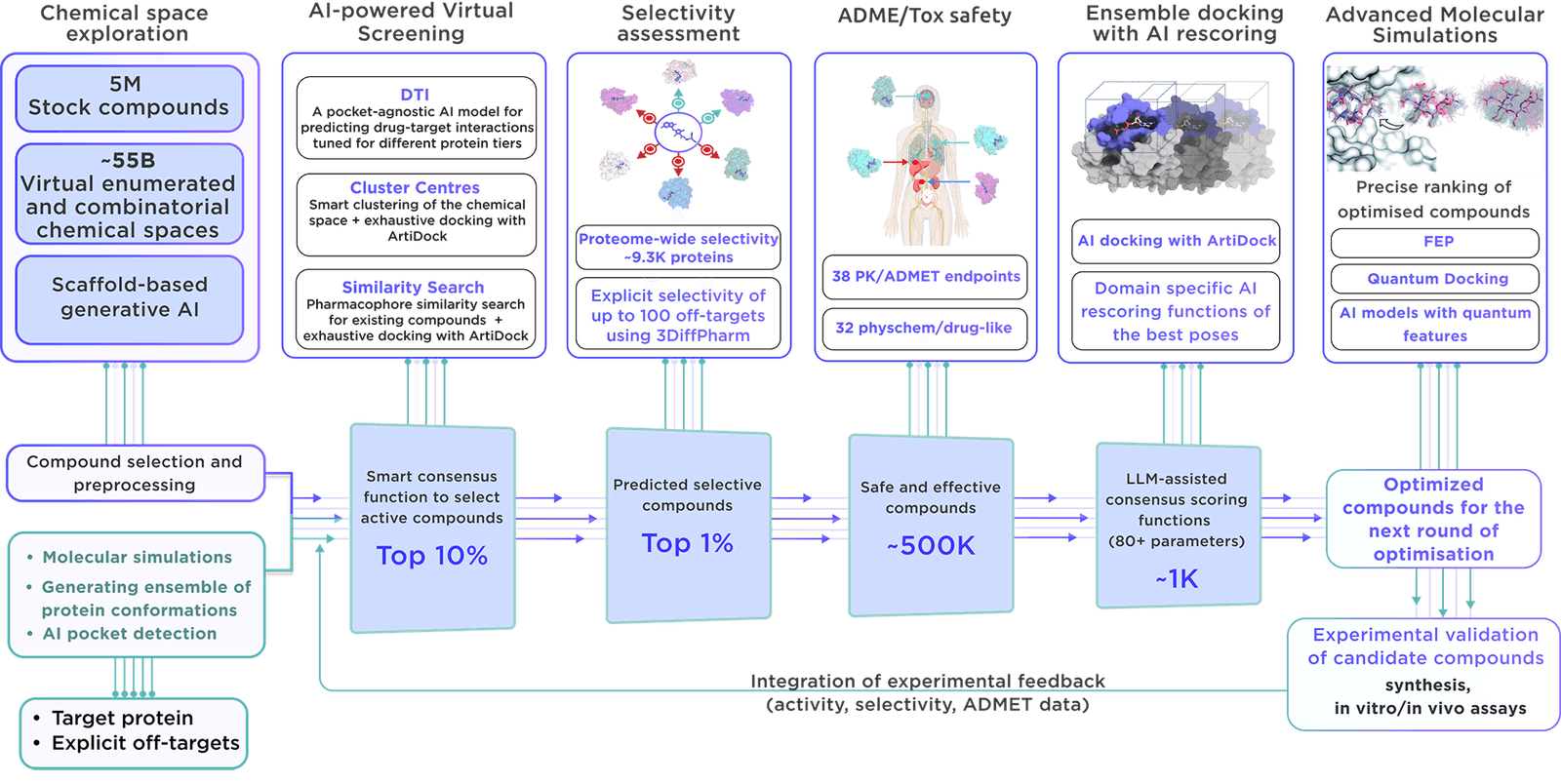
This comprehensive focused library is produced on demand with state-of-the-art virtual screening and parameter assessment technology driven by Receptor.AI drug discovery platform. This approach outperforms traditional methods and provides higher-quality compounds with superior activity, selectivity and safety.
We carefully select specific compounds from a vast collection of over 60 billion molecules in virtual chemical space. Reaxense helps in synthesizing and delivering these compounds.
The library includes a list of the most effective modulators, each annotated with 38 ADME-Tox and 32 physicochemical and drug-likeness parameters. Furthermore, each compound is shown with its optimal docking poses, affinity scores, and activity scores, offering a detailed summary.
We utilise our cutting-edge, exclusive workflow to develop focused libraries.
Our strategy employs molecular simulations to explore an extensive range of proteins, capturing their dynamics both individually and within complexes with other proteins. Through ensemble virtual screening, we address proteins' conformational mobility, uncovering key binding sites at both functional regions and remote allosteric locations. This comprehensive investigation ensures a thorough assessment of all potential mechanisms of action, with the goal of discovering innovative therapeutic targets and lead molecules across across diverse biological functions.
Several key aspects differentiate our library:
- Receptor.AI compiles an all-encompassing dataset on the target protein, including historical experiments, literature data, known ligands, and structural insights, maximising the chances of prioritising the most pertinent compounds.
- The platform employs state-of-the-art molecular simulations to identify potential binding sites, ensuring the focused library is primed for discovering allosteric inhibitors and binders of concealed pockets.
- Over 50 customisable AI models, thoroughly evaluated in various drug discovery endeavours and research projects, make Receptor.AI both efficient and accurate. This technology is integral to the development of our focused libraries.
- In addition to generating focused libraries, Receptor.AI offers a full range of services and solutions for every step of preclinical drug discovery, with a pricing model based on success, thereby reducing risk and promoting joint project success.
Receptor.AI
Q9ULJ6
UPID:
ZMIZ1_HUMAN
ALTERNATIVE NAMES:
PIAS-like protein Zimp10; Retinoic acid-induced protein 17
ALTERNATIVE UPACC:
Q9ULJ6; Q5JSH9; Q7Z7E6